How to use
How to run Jupyter Notebook
How to run Jupyter Lab
How to run Jupyter Notebook in a virtual environment
Where does it save ImageNet data?
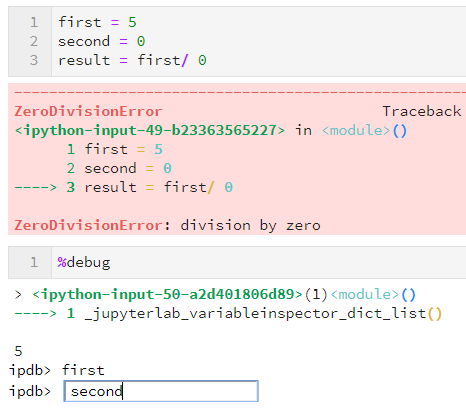
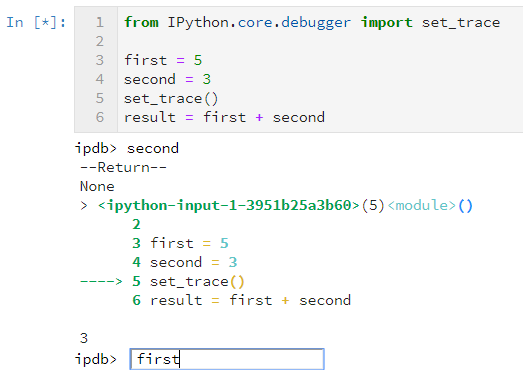
How to debug in Jupyter Notebook
Last updated