BakeryCashier
Bread Auto-Calculator
Date: 2022/06/20
Author: Song Yeong Won/ Song Tae Woong
Github: repository link
Demo Video: Youtube link
Introduction
In this project, we want to implement an automatic bread calculator for quick and quick work processing. This program aims to increase work efficiency by quickly and accurately detecting and calculating bread in bakery stores. In addition, it is intended to reduce the inconvenience of having to take direct barcodes and increase the convenience of users. A total of five types of bread were used as objects in this program, and Apple in the tree at Handong University was used.
Since the YOLOv5 model was directly trained and used through Custom-data, the DarkLabel 2.4 program was used to generate additional training data. We used YOLOv5 open source and Python via Anaconda virtual environment in Visual Studio Code.
1. Requirement
Hardware
NVDIA GeForce RTX 3080
HD Pro Webcam C920
Environment constraint
Camera angle : 37.5 degree
Camera height : 47[cm] from Tray
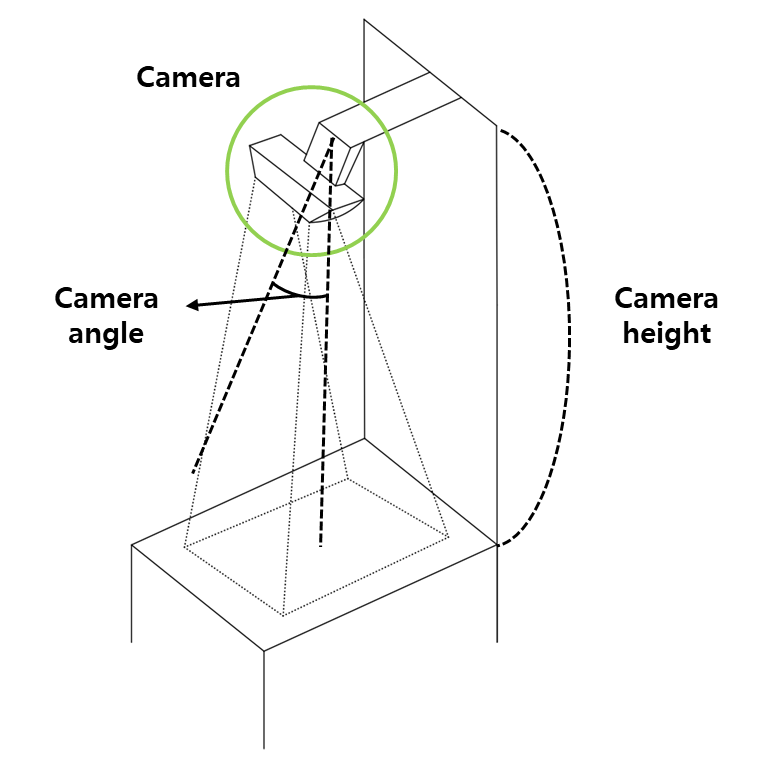
Figure 1. Experiment Environment
Software Installation
software specification as follow :
CUDA 11.6
cudatoolkit 11.3.1
Python 3.9.12
Pytorch 1.10
YOLOv5l model
Anaconda settings
before starting, check if the GPU driver for the cuda version is installed.
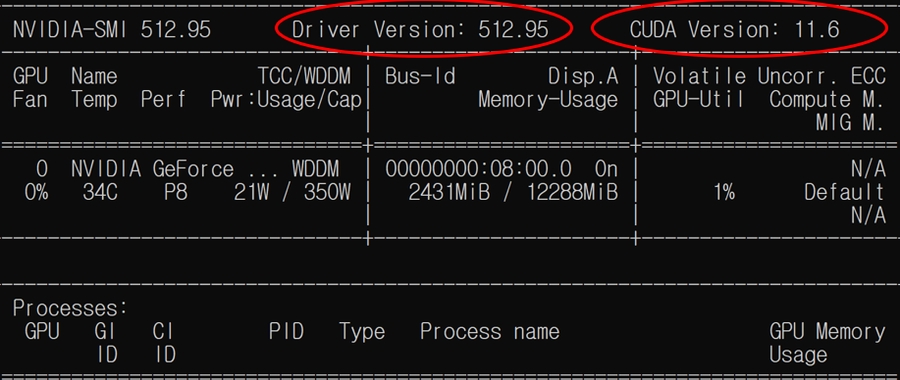
Figure 2. Check CUDA Version
check your cuda version and donwload nvidia driver click here
YOLOv5 Installation
Go to YOLOv5 github (https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) and download Repository as below. After entering the /yolov5-master folder, copy the path address. Then executing Anaconda prompt in administrator mode, execute the code below sequentially.
Labeling
DarkLabel2.4
The DarkLabel 2.4 program was used to generate custom data. Using this program, bounding box labeling was performed directly for each frame of the video to create an image and label dataset. Compared to other labeling programs, labeling work through images is possible, so it is possible to generate a lot of training data quickly.
Go to DarkLabel 2.4 and download the DarkLabel 2.4 program below. if it is not available, please download here
Figure 3. DarkLabel2.4
After executing DarkLabel.exe, labeling is performed using the desired image or image.
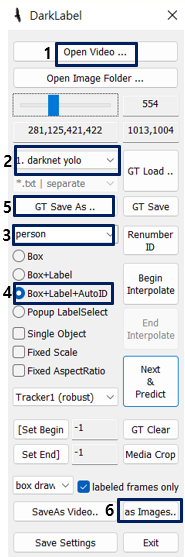
Figure 4. DarkLabel2.4 Tool
Image file path for using image files
Using Darknet yolo labeling method
To using your customized labels for model training, the number of data and class name of coco dataset must be changed.
change the Number 0 - 5 COCO dataset classes : [‘person’, ‘bicycle’, ‘car’, ‘motorcycle’, ‘airplane’, ‘bus’] -> 6 COCO based custom dataset classes : [‘Apple Tart’, ‘Croissant’, ‘Chocolate’, ‘Bagel’, ‘White Donut’, ‘Pretzel’]
save labels
save images
for example using darklabel2.4 program :

Figure 5. Example of using DarkLabel2.4
If you keep pressing the space, you can quickly label the image because you keep tracking the image with the bounding box over every frame and draw the bounding box. However, if an object is moved or obscured, it will not be accurate tracking, so such frames should be re-run after removing the image labeling.
2. Training Procedure
Pretrained Checkpoints
The model should be selected in consideration of the accuracy and processing speed suitable for the purpose. This project used the YOLOv5l model. The model should be appropriately selected according to GPU Driver performance. It is also important to select the batch size that GPU cuda memory can allocate. Batch size = 4 was applied to this model learning. If you use a better hardware GPU driver, you can use a YOLOv5l or higher model.
The results of precision and recall learned through the YOLOv5l model will be mentioned in the 4. Evaluation part.
Model
size (pixels)
mAPval 0.5:0.95
mAPval 0.5
Speed CPU b1 (ms)
Speed V100 b1 (ms)
Speed V100 b32 (ms)
params (M)
FLOPs @640 (B)
Table 1. Model Performance
Further more information : Click here
2.1 Customize datasets

Images data
Labels
For training using the YOLOv5 model, an image file and a labeling coordinate file are required as shown in Figure 6. We previously generated the data in Figure 6 using the Dark Label program. Looking at the labeling coordinate file, it fits the YOLOv5 model as below.

Figure 7. Label txt file
Total number of Image dataset : 5,546
Total number of labeling dataset : 5,546
2.2 Split Train and Validation set
Create a datasets folder at the same location as the yolov5-master folder.
Train image dataset path : datasets > bakery > images > train
Train label dataset path : datasets > bakery > labels> train
Val image dataset path : datasets > bakery > images > val
Val label dataset path : datasets > bakery > labels> val

Figure 8. Datasets path
2.3 create customized yaml file
create new bakery.yaml file. (path : ./data)
Figure 9. yaml file path
check the train and val path as follow.
2.4 Model Training
When you start training, you must select img size, batch size, epochs, and model. Make sure that the bakery.yaml path is correct based on the current path running the above code. In addition, the model of yolov5 must be selected, and it can be selected from four types: s,m,l,x, and yolov5l model was used for this training. Finally, it is also important to determine the batch size. The batch size must be selected according to GPU or CPU performance, and a "cuda out of memory" error will occur if the batch size is set too large. Training is possible while gradually reducing the batch size. If the epoch is set very large, there is a risk of overfitting, and if the epoch is set low, it may become underfitting. Trial and error is required for optimal model training.
The Figure 10 below is an output window when only epoch 1 is executed. Train results and weight.pt files can be found in runs/train/exp (number).
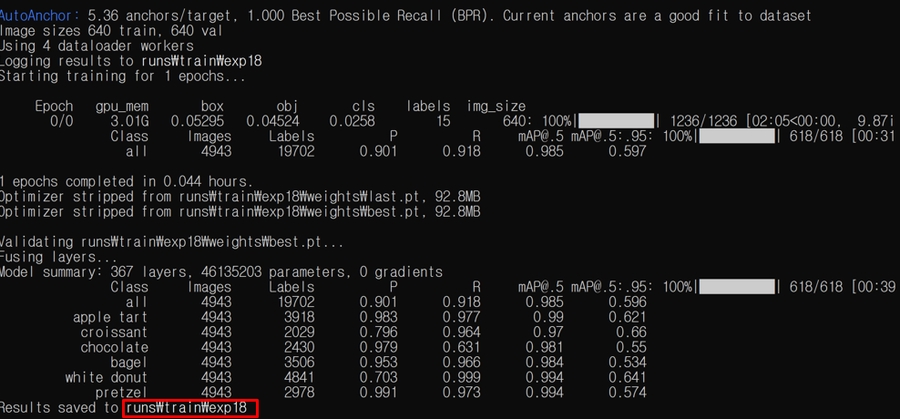
Figure 10. Model Training
2.5 Using Trained Weight.pt
When you proceed with model training, there are best.pt and last.pt in the file. The best.pt file is a model weight file that has the optimal training parameter weight. last.pt is the final model weight file when all training is done. If we set a lot of epochs, we used the most optimal best.pt because it could be overfitting at the end of training.
It can be seen that the weights file is generated in the runs/train/exp(number) path.

Figure 11. Trained weight file
We changed the best.pt file name to bakery.pt.
bakery.py file path : /yolov5-master
You can test through the weight.pt file trained through the code below.
Figure 12. Test
3. Algorithm
The algorithm has three main sections. Whole process of program algorithm as follows.
pre-processing
Rounding Tray
post-processing
Image Capture
Filtering Out of tray
Auto-calculation
Application
KAKAOPAY QR Code
Image Concatenation
Flowchart
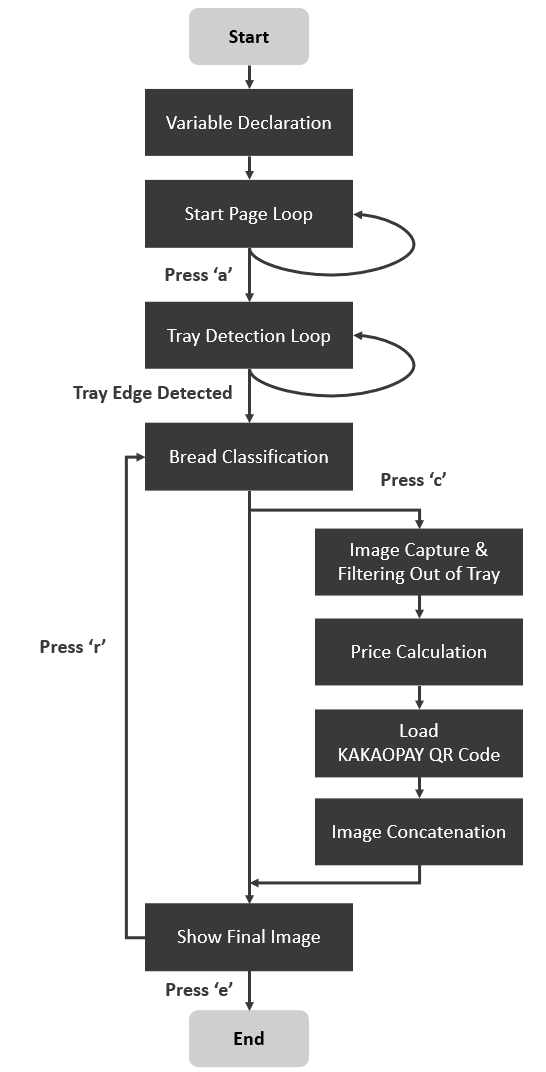
Figure 13. Flowchart
3.1 Pre-processing
Rounding Tray
The ROI area required for object detection should be set. First, find the four vertices of the rounding tray and draw a square to determine if an object exists in the square. For this algorithm, the openvInrange function and the HoughlineP function were used. Since the original image used is a BGR scale, the surrounding tray edge is extracted by first converting it to HSV and then adjusting Inrange to Hue, Saturation, and Value. Figure 14 (a) is an original frame image, and (b) is a result of converting to a binary image after Inrange processing. If firstFrame = 1 is the exact line of the tray, if not, repeat until firstFrame = 0 and extract the correct line. This is the tray detection loop represented in Figure 13. flowchart.
Rounding Tray using HoughlineP


Source Image (a)
After Inrange (b)
Figure 14. HoughLinesP
Finally, the HoughLinesP is adjusted to extract the line in the Inrange. Several lines are detected through HoughLineP, and we found and used the maximum, minimum x, and y values of all extracted straight lines because only the edge of the tray should be represented by one box. Therefore, the results are as follows.

Figure 15. Tray detection
3.2 post-processing
Image Capture
The first process of post-processing is image capture. When the 'c' key is pressed, the current frame is captured and object detection is performed on the frame. Since the frame image at the moment of capture is continuously stored, pressing the 'c' key continuously uses the stored image. When 'r' is pressed, the captured frame is initialized back into the current frame. Figure 16 is the result of object detection when the 'c' key is input.

Figure 16. Image Capture
Filtering Out of tray
We performed the out of tray filtering process for accurate calculation. We performed filtering using the center coordinates of the object detection rounding box. If the central coordinate of the bounding box was within the tray edge area, it was determined as inside, and if it existed outside, it was determined as outside. In Figure 17, objects existing outside the rounding tray are represented by a red binding box. Rounding Tray is a post-processing process that assumes a cash register where a real customer puts things up, and does not calculate objects that exist outside the cash register.

Figure 17. Filtering result
Auto-calculation
If you have distinguished the bread in the Rounding Tray after the Out of Tray filtering process, calculate the total price for the bread only. The class name existing for each frame may be returned as int(cls) in integer. Therefore, we sum the prices for all objects corresponding to the class number specified in advance.
If you have learned by adding more kinds of bread, you can add the class number and price to the list below.

Figure18. Class list
3.3 Application
We added display elements in consideration of actual commercial applications. Total price according to the total price was output, and Kakao Pay QR code was output so that actual consumers could pay. Figure 19 is the final result of combining three images: webcam image, qr code, and price. Looking at Figure 19, the total price was set at 7,800 won. This is a price measurement for only three objects in the Rounding Tray, and it can be seen that bread outside the Rounding Tray in red is not included in the total price price. Also, for bread with Inside Rounding Tray, the price is marked for each object.

Figure 19. Application Display
3.4 Customized detect.py
This is the final customized detect.py file.
4. Evaluation
In this project, we learned customized datasets through the YOLOv5l model, and the training performance was very good. As can be seen from the reproduction rate and precision graph shown below, model training shows very high values. The training evaluation was performed through the test video image, and (valid results) came out somehow. As the most important goal of this project was to recognize bread in real time and enable calculation, we achieved as much as expected in terms of speed and accuracy. Therefore, it was possible to implement a fast and accurate model through a low-cost webcam and GPU.
Figure 20 is the result of val execution. Both Precision and Recall showed a high performance of 99%. Since training was performed using images, there is a possibility that more than a few frames have the same image. Therefore, since similar images may be validated, the precision and reproduction rate were higher than expected.

Figure 20. Validation result
Figure 22 is a graph showing F1-Score after validation. F1-Score is a value representing the harmonic mean of precision and reproducibility. Precision is the ratio of what the model classifies as true that is true. It is the ratio of predicting that the model is true among the actual true reproduction rates. Accurate classification is possible by increasing precision. However, the higher the precision, the lower the reproduction rate. Therefore, precision and reproducibility are in a trade-off relationship. Since we have to accurately classify and accurately predict actual bread, the harmonic mean, which can reasonably consider precision and reproducibility, was used as an evaluation criterion for basic model performance.

Figure 21. Model Evaluation
Looking at Figure 22, the confidence of all classes is maintained above 0.8. Therefore, it can be confirmed that the actual bread type was accurately classified.

Figure 22. F1-score of Model
However, there are some issues that need to be fixed. First of all, in this project, we learned bread without wrapping paper. If it is packaged, it is expected that there will be difficulties in training because it is difficult to distinguish the reflection of light or the exact model of bread. If you want to learn and classify bread with wrappers, it is considered important to learn cropping or rotation, and to different images from various angles in addition to the original image. In addition, there are various models for one bread type, but in this project, we learned about one bread type using only one bread. In order to apply the results of the project in the actual store, a post-processing process that can distinguish bread from similar models of the same kind as more data is needed.
In this project, users can pay through QR code images. In order to implement it as an actual payment system, it is necessary to introduce an additional computer system.
5. Run Test Video
Finally, if you have completed training the data, data preprocessing, and post-processing, you can check it through real-time images by executing the following code.
Reference
YOLOv5 : [Click here](ultralytics/yolov5: YOLOv5 🚀 in PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > TFLite (github.com))
YOLOv5 installation : Click here
Appendix
video Demo Link
Final Demo video : Click here
Last updated