Tutorial: Train Yolo v5 with custom dataset
This tutorial is about learning how to train YOLO v5 ~ v8 with a custom dataset of Mask-Dataset.
This Tutorial works for both YOLOv5 and YOLOv8
Step 1. Install and Configure YOLO in local drive
Follow Tutorial: Installation of Yolov8
Step 2. Prepare Custom Dataset
Download Dataset and Label
We will use the Labeled Mask YOLO to detect people wearing mask.

This annotation file has 4 lines being each one referring to one specific face in the image. Let’s check the first line:
The first integer number (0) is the object class id. For this dataset, the class id 0 refers to the class “using mask” and the class id 1 refers to the “without mask” class. The following float numbers are the xywh bounding box coordinates. As one can see, these coordinates are normalized to [0, 1].
Download the dataset : Labeled Mask YOLO.
Create the folder
/datasetsin the same parent with the/yolov5folder. You already have this folder if you have trained coco128 in previous tutorial.Under the directory
/datasets, create a new folder for the MASK dataset. Then, copy the downloaded dataset under this folder. Example:/datasets/dataset_mask/archive/obj/

The dataset is indeed a bunch of images and respective annotation files:
Visualize Train Dataset image with label
Under the folder
/datasets/create the following python file (visualizeLabel.py) to view images and labels. Download code here
You will see this result

Step 3 — Split Dataset
The YOLOv5 training process will use the training subset to actually learn how to detect objects. The validation dataset is used to check the model performance during the training.
We need to split this data into two groups for training model: training and validation.
About 90% of the images will be copied to the folder
/training/.The remaining images (10% of the full data) will be saved in the folder
/validation/.
For the inference dataset, you can use any images with people wearing mask.
Under the directory
datasets/create the following python filesplit_data.py. Download [code here]https://github.com/ykkimhgu/DLIP-src/blob/main/Tutorial_Pytorch/split_data.py)This code will save image files under the folder
/images/folder and label data under the folder/labels/Under each folders,
/trainingand/validationdatasets will be splitted
Run the following script and check your folders

Step 4. Training configuration file
The next step is creating a text file called maskdataset.yaml inside the yolov5 directory with the following content. Download code here
Step 5. Running the train
It is time to actually run the train:
change bath number and epochs number for better training
Finally, in the end, we have the following output:

Now, confirm that you have a yolov5_ws/yolov5/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt file:
Depending on the number of runs, it can be under
/train/exp#/weights/best.pt, where #:number of expFor my PC, it was exp3

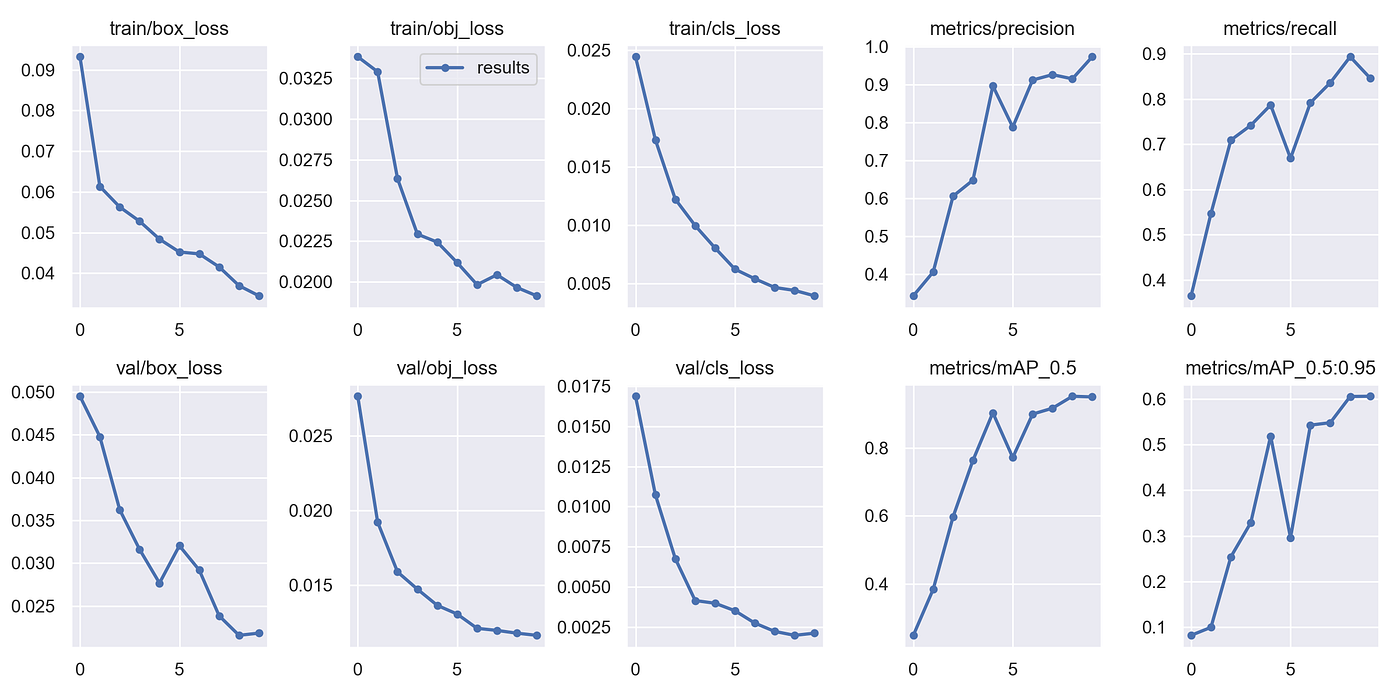
Also, check the output of runs/train/exp/results.png which demonstrates the model performance indicators during the training:
Step 6. Test the model (Inference)
Now we have our model trained with the Labeled Mask dataset, it is time to get some predictions. This can be easily done using an out-of-the-box YOLOv5 script specially designed for this:
Download a test image here and copy the file under the folder of yolov5/data/images
Run the CLI
Your result image will be saved under runs/detect/exp

NEXT
Test trained YOLO with webcam
Last updated