Tutorial: OpenCv (Python) Basics
Tutorial: OpenCV (Python) Basics
Preparation
Basics of Python & Numpy
Python Basics
Numpy Basics
Configuration
Source code and images
Download
Project and Data Folder
Running the source code
Basic Image Processing
(*.py) Read / Write / Display Image and Video
(*.ipyn) Read / Write / Display Image and Video
Import OpenCV Library
(for COLAB only) Upload Image Files in Colab server
Read Image File
Display Image using matplot plt.imshow()
plt.imshow()Display Image: (for .py only) OpenCV imshow()
Display Image: (for Colab only) cv2_imshow()
Capturing Video
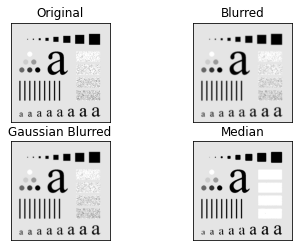
Spatial Filter
Example Code
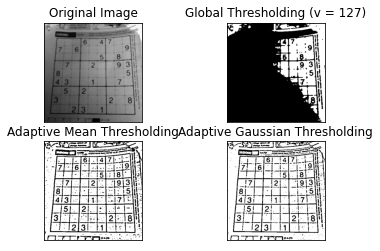
Thresholding
Manual Local Threshold
Example Code

Adaptive Threshold
Example code
Plot Histogram
Example Code
Morphology
Example Code

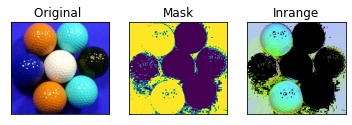
Color Segmentation (InRange)
Example code
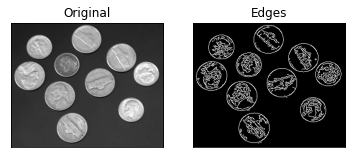
Edge & Line & Circle Detection
Edge Detection
Example code 1
Example code 2
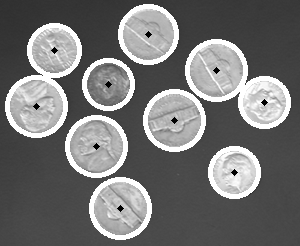
Circle Detection
Example code
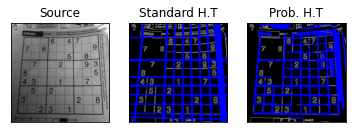
Line Detection
Example code
Exercise
Beginner Level Exercise
Exercise 1

Example 2

Example 3

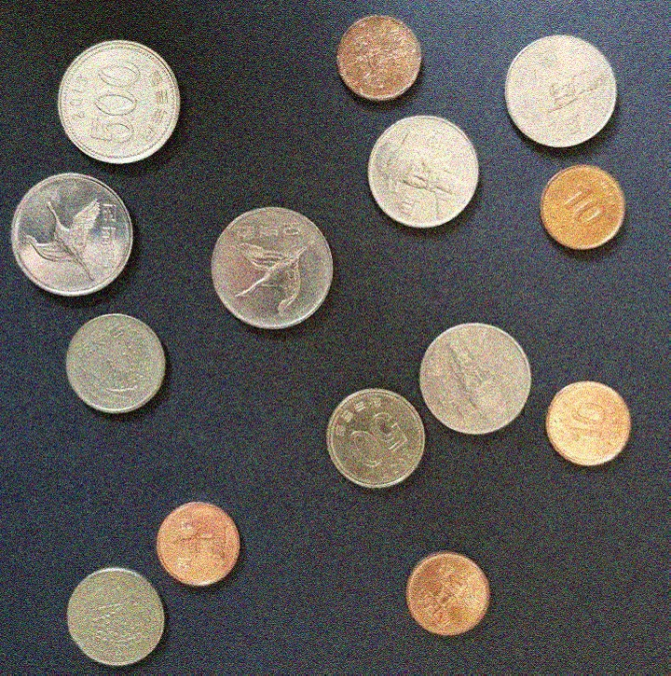
Intermediate Level Exercise
Exercise: Count number of coins and calculate the total amount

Last updated