Debugging in uVision
Overview
Preparation
#include "stm32f4xx.h"
#define LED_PIN 5 //LD2
#define BUTTON_PIN 13
void RCC_HSI_init(void); //defined in ecRcc.h
void RCC_GPIOA_enable(void);
void RCC_GPIOC_enable(void);
int main(void) {
/* Part 1. RCC GPIOA Register Setting */
RCC_GPIOA_enable();
RCC_GPIOC_enable();
/* Part 2. GPIO Register Setting for OUTPUT*/
// GPIO Mode Register
GPIOA->MODER &= ~(3UL<<(2*LED_PIN)); // Clear '00' for Pin 5
GPIOA->MODER |= 1UL<<(2*LED_PIN); // Set '01' for Pin 5
// GPIO Output Type Register
GPIOA->OTYPER &= ~(1UL<<LED_PIN); // 0:Push-Pull
// GPIO Pull-Up/Pull-Down Register
GPIOA->PUPDR &= ~(3UL<<(2*LED_PIN)); // 00: none
// GPIO Output Speed Register
GPIOA->OSPEEDR &= ~(3UL<<(2*LED_PIN));
GPIOA->OSPEEDR |= 2UL<<(2*LED_PIN); //10:Fast Speed
/* Part 3. GPIO Register Setting for INPUT*/
// GPIO Mode Register
GPIOC->MODER &= ~(3UL<<(2*BUTTON_PIN)); // 00: Input
// GPIO Pull-Up/Pull-Down Register
GPIOC->PUPDR &= ~(3UL<<(2*BUTTON_PIN));
GPIOC->PUPDR |= 2UL<<(2*BUTTON_PIN); // 10: Pull-down
/* Part 4. Deal loop */
while(1){
unsigned int btVal=0;
//Read bit value of Button
btVal=(GPIOC->IDR) & (1UL << BUTTON_PIN);
if(btVal == 0)
GPIOA->ODR |= (1UL << LED_PIN);
else
GPIOA->ODR &= ~(1UL << LED_PIN);
}
}
void RCC_GPIOA_enable()
{
// HSI is used as system clock
RCC_HSI_init();
// RCC Peripheral Clock for GPIO_A Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR |= RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIOAEN;
}
void RCC_GPIOC_enable()
{
// HSI is used as system clock
RCC_HSI_init();
// RCC Peripheral Clock for GPIO_A Enable
RCC->AHB1ENR |= RCC_AHB1ENR_GPIOCEN;
}
void RCC_HSI_init() {
// Enable High Speed Internal Clock (HSI = 16 MHz)
RCC->CR |= ((uint32_t)RCC_CR_HSION);
// wait until HSI is ready
while ( (RCC->CR & (uint32_t) RCC_CR_HSIRDY) == 0 ) {;}
// Select HSI as system clock source
RCC->CFGR &= (uint32_t)(~RCC_CFGR_SW);
RCC->CFGR |= (uint32_t)RCC_CFGR_SW_HSI;
// Wait till HSI is used as system clock source
while ((RCC->CFGR & (uint32_t)RCC_CFGR_SWS) != 0 );
}Software vs Hardware Debug
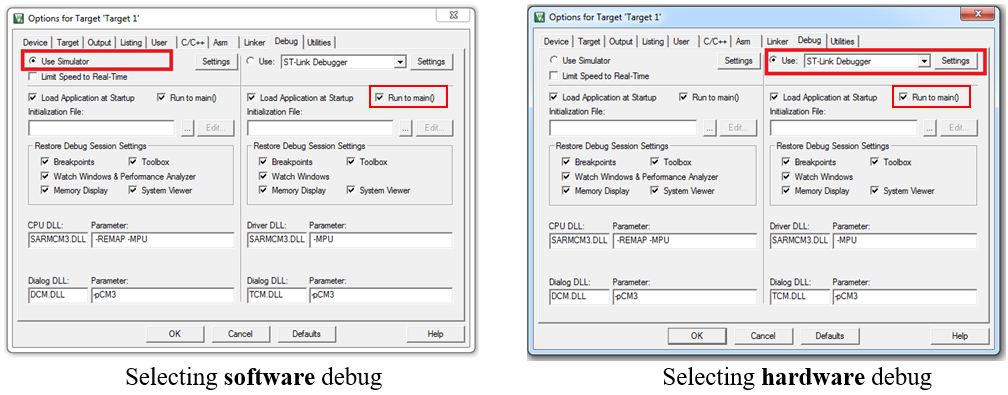
Debug Control
Compile, Debug, and Run
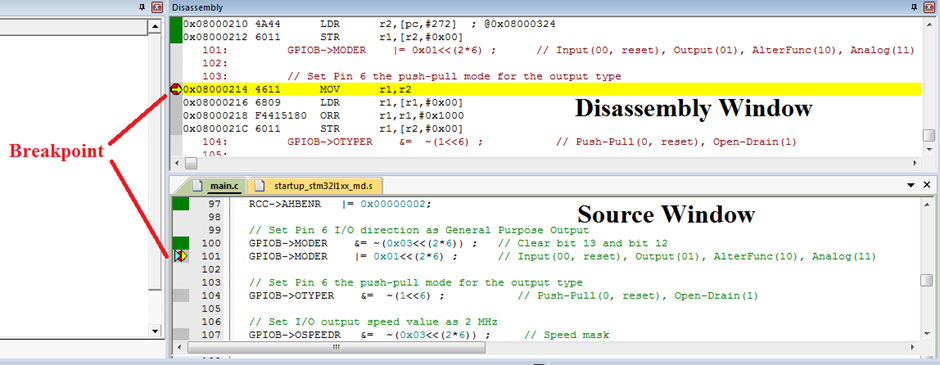

image
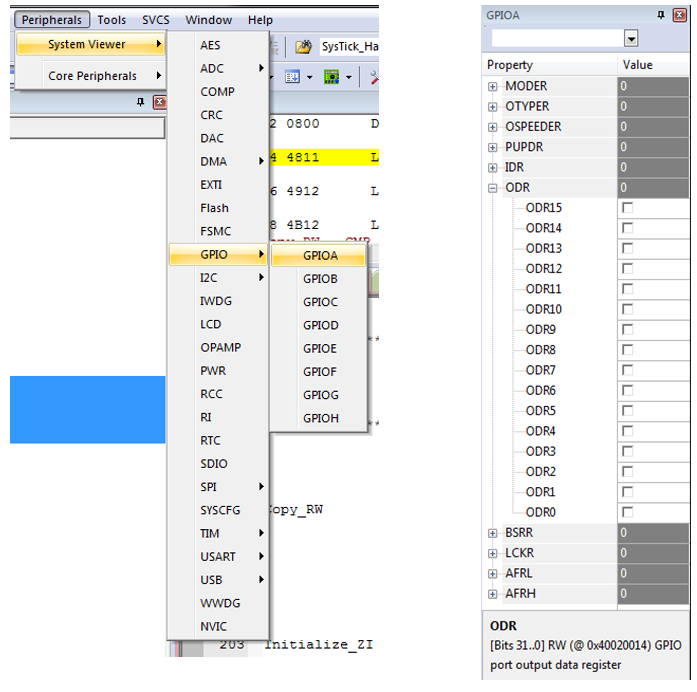
Pheripheral Registers
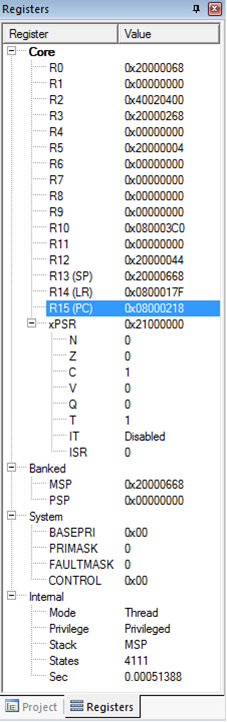
Processor Registers
Core Registers
xPSR
Description
Last updated