// State definition
#define S0 0
#define S1 1
// Address number of output in array
#define PWM 0
#define LED 1
const int ledPin = 13;
const int pwmPin = 11;
const int btnPin = 3;
unsigned char state = S0;
unsigned char nextstate = S0;
unsigned char input = 0;
unsigned char ledOut = LOW;
unsigned char pwmOut = 0;
// State table definition
typedef struct {
uint32_t next[2]; // nextstate = FSM[state].next[input]
uint32_t out[2][2]; // output = FSM[state].out[input][PWM or LED]
} State_t;
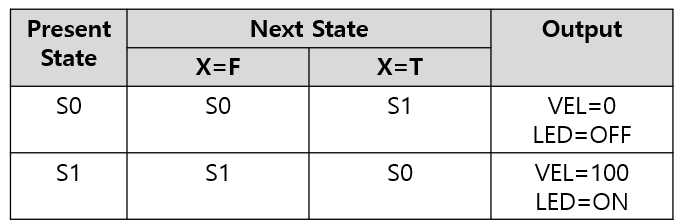
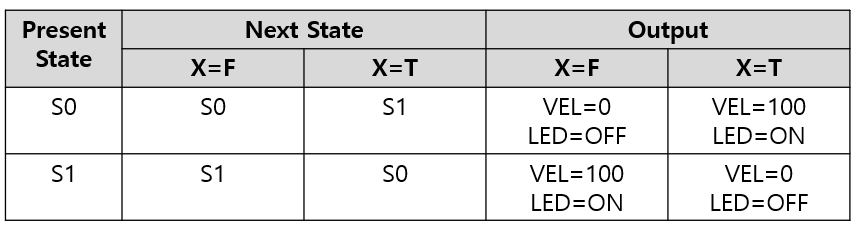
State_t FSM[2] = {
{ {S0, S1}, {{0 , LOW }, {160, HIGH}} },
{ {S1, S0}, {{160, HIGH}, {0 , LOW }} }
};
void setup() {
// initialize the LED pin as an output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// Initialize pwm pin as an output:
pinMode(pwmPin, OUTPUT);
// initialize the pushbutton pin as an interrupt input:
pinMode(btnPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(btnPin), pressed, FALLING);
}
void loop() {
// First, Output of current State. Then Update next state. Repeat
// 1. Output State
stateOutput();
analogWrite(pwmPin, pwmOut);
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledOut);
// 2. Update State <-- Next State
nextState();
delay(1000);
}
void pressed() {
input = 1;
}
void nextState() {
nextstate = FSM[state].next[input];
state = nextstate;
// Intialize Button Pressed
input = 0;
}
void stateOutput() {
pwmOut = FSM[state].out[input][PWM];
ledOut = FSM[state].out[input][LED];
}